6G (Sixth Generation Wireless) is the next generation of mobile communication technology, expected to succeed 5G and 5G-Advanced around 2030.
It represents a convergence of communication, computation, sensing, and artificial intelligence, enabling ultra-high-speed, ultra-low-latency, and intelligent global connectivity.
Goal:
6G will connect people, devices, machines, and environments in real time — integrating the physical, digital, and biological worlds through intelligent networks.
Evolution from 1G to 6G
| Generation | Era | Core Technology | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1G | 1980s | Analog cellular | Voice only |
| 2G | 1990s | Digital GSM/CDMA | Voice + SMS |
| 3G | 2000s | WCDMA, CDMA2000 | Mobile data & internet |
| 4G (LTE) | 2010s | OFDM, MIMO | Broadband internet, HD video |
| 5G | 2020s | Massive MIMO, mmWave, Network slicing | eMBB, URLLC, mMTC |
| 6G | ~2030 | THz bands, AI-native, Integrated Sensing | Intelligence-centric, ultra-connectivity, holographic communication |
6G Core Objectives
- 100× improvement in speed and latency over 5G.
- Integration of AI/ML in every layer — “AI-native networks.”
- Communication + Sensing + Computing unified in one platform.
- Ubiquitous coverage — including space, air, sea, and underground.
- Extreme energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Trust, security, and privacy built into architecture.
Target Specifications (Indicative Values)
| Parameter | 5G Benchmark | 6G Target |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Data Rate | 20 Gbps | 100–1,000 Gbps (1 Tbps in short range) |
| User Data Rate | 100 Mbps | 1–10 Gbps |
| Latency | 1 ms | 0.1 ms (100 microseconds) |
| Reliability | 99.999% | 99.99999% |
| Connection Density | 1 million devices/km² | 10 million devices/km² |
| Mobility Support | Up to 500 km/h | Up to 1,000 km/h |
| Spectral Efficiency | ~30 bps/Hz | >100 bps/Hz |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | 100× improvement |
| Coverage | Terrestrial | Terrestrial + Non-Terrestrial (satellite, UAVs) |
Key Technologies Enabling 6G
1. Terahertz (THz) Communication (100 GHz–1 THz)
- Extremely wide bandwidth for ultra-fast data rates.
- Used for holographic, tactile internet, and short-range ultra-high-capacity links.
- Challenge: high path loss and poor penetration (requires advanced beamforming).
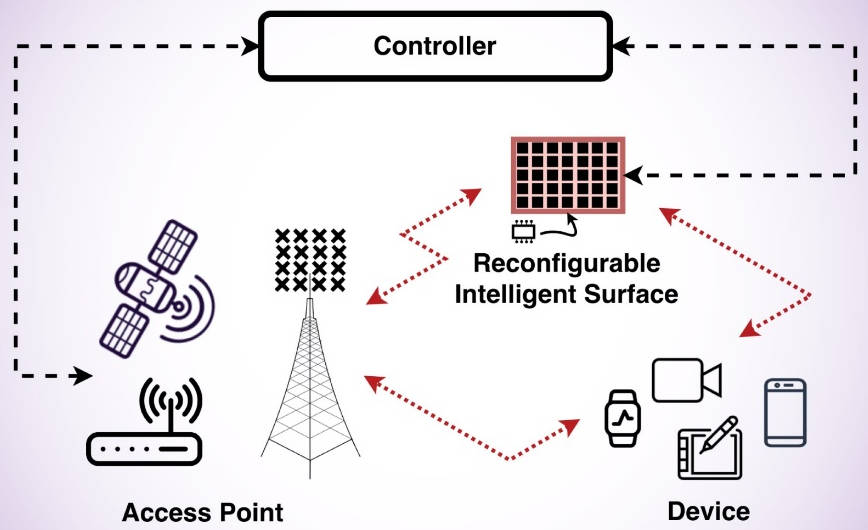
2. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS)
- Smart surfaces made of meta-materials that can reflect, refract, and shape radio waves.
- Enable control of wireless environments (like “programmable walls”).
- Improve coverage, reduce interference, and boost energy efficiency.
3. Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC)
- Combines radar-like sensing with data communication.
- The same signals used for both detecting objects/environment and transmitting data.
- Enables localization, tracking, gesture recognition, and environmental mapping.
4. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning (AI/ML)
- Embedded in every layer: from physical to application.
- Functions include self-optimizing networks, predictive resource allocation, and automated network maintenance.
- Leads to AI-native architectures — networks that learn and adapt autonomously.
5. Massive MIMO and Holographic Beamforming
- Use of hundreds or thousands of antennas for spatial multiplexing.
- “Holographic MIMO” uses continuous surfaces of antennas for ultra-fine beam control.
6. Edge Computing & Distributed Intelligence
- Moves data processing close to the user (edge or device level).
- Reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and enhances privacy.
- AI algorithms distributed across cloud–edge–device continuum.
7. Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN)
- Integration of LEO/MEO satellites, UAVs (drones), and HAPS (High-Altitude Platforms) with terrestrial 6G.
- Ensures global coverage in oceans, mountains, and rural areas.
8. Quantum Communication and Security
- Use of quantum key distribution (QKD) for ultra-secure links.
- Quantum-safe encryption to protect against future quantum computers.
9. Energy Harvesting and Green Networking
- Use of solar, RF energy, or kinetic energy to power network nodes.
- Dynamic sleep modes, AI-controlled power usage.
- Aim: carbon-neutral communication networks.
Network Architecture (Conceptual)
A. AI-Native Architecture
- AI is not an add-on but integrated into control planes, user planes, and management layers.
- Functions: prediction, optimization, anomaly detection, self-healing.
B. Cloud-Edge Continuum
- Unified cloud and edge computing environments.
- Services are deployed dynamically where needed (edge, cloud, or device).
C. Disaggregated and Virtualized RAN
- Radio Access Network (RAN) functions are split and virtualized.
- Enables flexible deployment, cost reduction, and open interoperability (Open RAN).
D. Network Slicing
- Creation of multiple virtual networks over shared infrastructure.
- Each slice optimized for specific requirements (e.g., AR/VR vs IoT vs autonomous vehicles).
E. Integrated Terrestrial–Non-Terrestrial Infrastructure
- Ground base stations + satellites + aerial relays function as a single cohesive system.
Major Use Cases of 6G
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Immersive XR / Holographic Communication | 3D telepresence, tactile internet, metaverse experiences | Holographic meetings, remote education |
| Autonomous Systems & Mobility | Real-time vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and drone control | Self-driving cars, drone swarms |
| Industrial Automation (Industry 5.0) | AI-driven, human-collaborative factories | Smart manufacturing, predictive maintenance |
| Remote Healthcare | Remote diagnosis, surgery with haptic feedback | Tele-robotic surgery |
| Smart Cities / Infrastructure | Intelligent traffic, energy management, safety systems | IoT sensors, digital twins |
| Global Broadband Connectivity | Coverage for rural and remote areas | Satellite-aided internet |
| Environmental Monitoring | Climate, pollution, disaster management | Sensor networks, UAV swarms |
| Next-gen IoT & Bio-Internet of Things (Bio-IoT) | Integration of biological sensors and implants | Smart wearables, health monitoring chips |
Challenges in Developing 6G
1. Technical Challenges
- THz signal propagation loss and atmospheric absorption.
- Miniaturization and cost of THz hardware.
- Interference management for dense networks.
- Real-time AI model training within limited energy budgets.
2. Spectrum and Regulation
- Allocation of new spectrum bands (sub-THz, visible light).
- Need for global harmonization by ITU and 3GPP.
- Licensing and sharing between terrestrial and non-terrestrial systems.
3. Security and Privacy
- Attack surface grows due to pervasive connectivity.
- AI systems can be manipulated (adversarial attacks).
- Massive sensor networks raise privacy concerns.
4. Energy & Sustainability
- Higher frequencies and data rates increase power demand.
- Green hardware and smart energy management are essential.
5. Economic and Deployment
- Infrastructure cost, especially in developing regions.
- Need for backward compatibility and transition from 5G.
Standardization and Timeline
| Stage | Organization | Expected Period | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5G-Advanced (Release 18/19) | 3GPP | 2024–2026 | Transitional phase toward 6G |
| IMT-2030 Vision | ITU-R | 2025 | Defines global 6G framework |
| Early 6G Standardization | 3GPP Release 20 | 2027–2028 | Defines air interface, architecture |
| Pilot Deployments | Vendors / Operators | 2028–2029 | Test networks and devices |
| Commercial Launch | Global | ~2030 | First 6G networks |
Security and Trust Framework
6G will require end-to-end trust mechanisms:
- Zero-Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA)
- Blockchain-based identity management
- AI-driven intrusion detection
- Quantum-resistant encryption
- Secure multi-party computation for data privacy
Sustainability and Green Networking
6G is expected to:
- Reduce energy per bit by 100× compared to 5G.
- Utilize renewable power for base stations.
- Support circular economy (recycling hardware materials).
- Include AI energy optimizers for traffic and network load balancing.
Impact on Society and Industry
Economic
- Enables new trillion-dollar markets (XR, AIoT, smart manufacturing).
- Drives automation and efficiency across sectors.
Social
- Improved healthcare, education, disaster management, and accessibility.
- Risk of digital divide if infrastructure is unevenly distributed.
Environmental
- Real-time monitoring of pollution, energy use, and resource management.
- Can aid sustainability goals if energy efficiency is achieved.
Role in Developing Regions (e.g., Pakistan & Similar Countries)
- Bridging Connectivity Gaps: Integration of satellite and terrestrial 6G can cover remote areas.
- Smart Agriculture: Sensors and drones for irrigation, crop monitoring.
- Education & Health Access: XR-based remote learning and telemedicine.
- Energy Constraints: Emphasis on energy-efficient designs and renewable-powered base stations.
- Policy Need: Spectrum reform, public-private partnerships, and local R&D investment.
Future Beyond 6G
Researchers are already discussing:
- 7G Concepts: Integration of quantum communication, AI-driven cognition, and bio-cybernetic interfaces.
- Human-Machine Symbiosis: Neural interfaces connecting brains directly to networks.
- Ubiquitous Intelligence: Every object and environment becomes a “smart entity” communicating autonomously.
Leave a Reply